IFTTT
IFTTT
Prerequisites
To be able to receive events from IFTTT, your Home Assistant instance needs to be accessible from the web and you need to have the external URL configured, or use your Nabu Casa account’s webhook URL from the IFTTT integration.
Configuration
To add the IFTTT integration to your Home Assistant instance, use this My button:
If the above My button doesn’t work, you can also perform the following steps manually:
-
Browse to your Home Assistant instance.
-
In the bottom right corner, select the
Add Integration button. -
From the list, select IFTTT.
-
Follow the instructions on screen to complete the setup.
Receiving events from IFTTT
Events coming in from IFTTT will be available as events in Home Assistant and are fired as ifttt_webhook_received. The data specified in the IFTTT recipe Body section will be available as the event data. You can use this event to trigger automations. Use POST as method.
For example, set the body of the IFTTT webhook to:
{ "action": "call_service", "service": "light.turn_on", "entity_id": "light.living_room" }
You then need to consume that incoming information with the following automation:
automation:
- alias: "The optional automation alias"
triggers:
- trigger: event
event_type: ifttt_webhook_received
event_data:
action: call_service # the same action 'name' you used in the Body section of the IFTTT recipe
actions:
- action: '{{ trigger.event.data.service }}'
target:
entity_id: '{{ trigger.event.data.entity_id }}'
Sending events to IFTTT
# Example configuration.yaml entry
ifttt:
key: YOUR_API_KEY
key is your API key which can be obtained by viewing the Settings of the Webhooks applet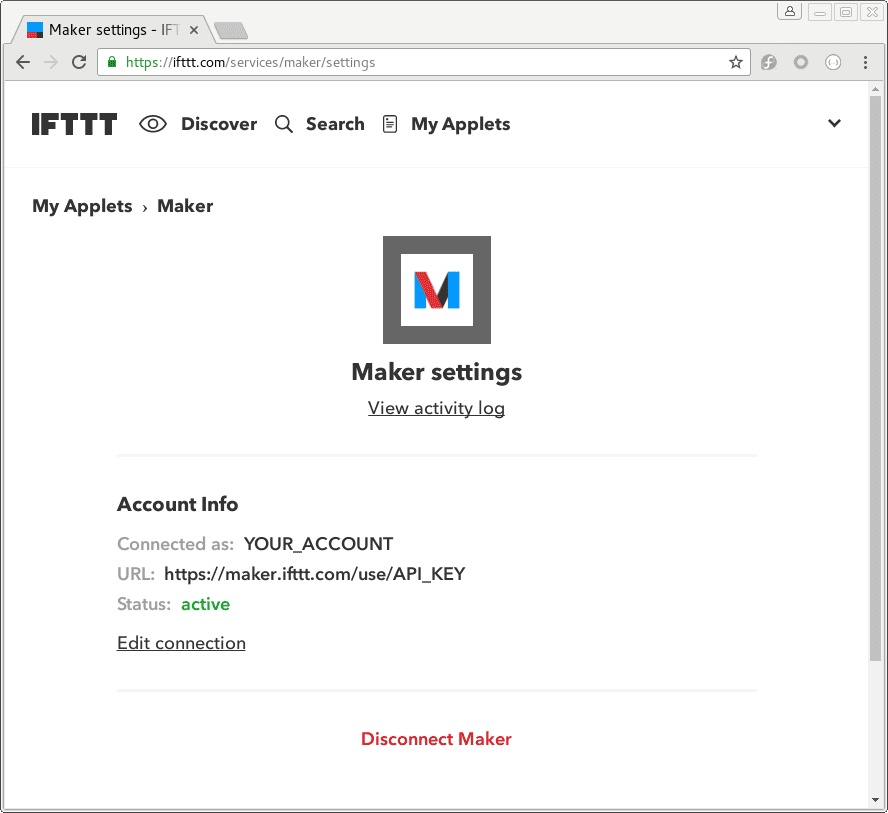
Once you have added your key to your configuration.yamlThe configuration.yaml file is the main configuration file for Home Assistant. It lists the integrations to be loaded and their specific configurations. In some cases, the configuration needs to be edited manually directly in the configuration.yaml file. Most integrations can be configured in the UI. [Learn more] file, restart your Home Assistant instance. This will load up the IFTTT integration and make an action available to trigger events in IFTTT.
After restarting the server, be sure to watch the console for any logging errors that show up in red, white or yellow.
Multiple IFTTT keys
If you have multiple IFTTT users you can specify multiple IFTTT keys with:
# Example configuration.yaml entry
ifttt:
key:
YOUR_KEY_NAME1: YOUR_API_KEY1
YOUR_KEY_NAME2: YOUR_API_KEY2
Testing your trigger
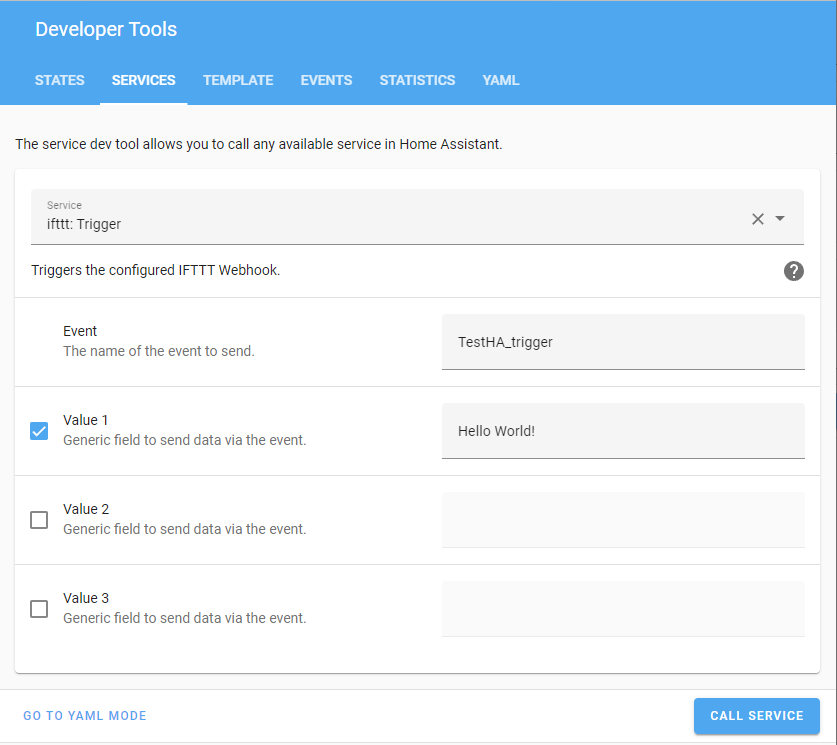
You can use Developer tools to test your WebhooksIFTTT: Trigger as the action and fill in the following values:
When your screen looks like this, select the Perform action button.
By default, the trigger is sent to all the API keys from configuration.yamlThe configuration.yaml file is the main configuration file for Home Assistant. It lists the integrations to be loaded and their specific configurations. In some cases, the configuration needs to be edited manually directly in the configuration.yaml file. Most integrations can be configured in the UI. [Learn more]. If you
want to send the trigger to a specific key use the target field:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| domain | ifttt |
| service | trigger |
| data | {"event": "EventName", "value1": "Hello World", "target": "YOUR_KEY_NAME1"} |
The target field can contain a single key name or a list of key names.
Setting up an applet
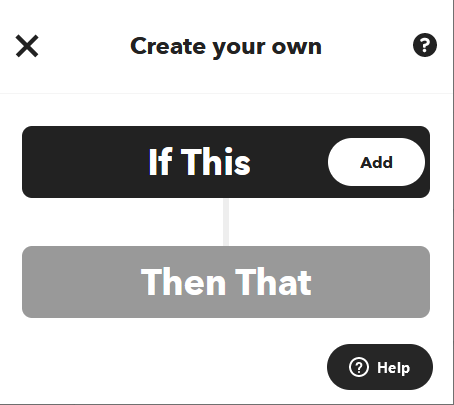
Press the Create button and Add on If This. Search for Webhooks.
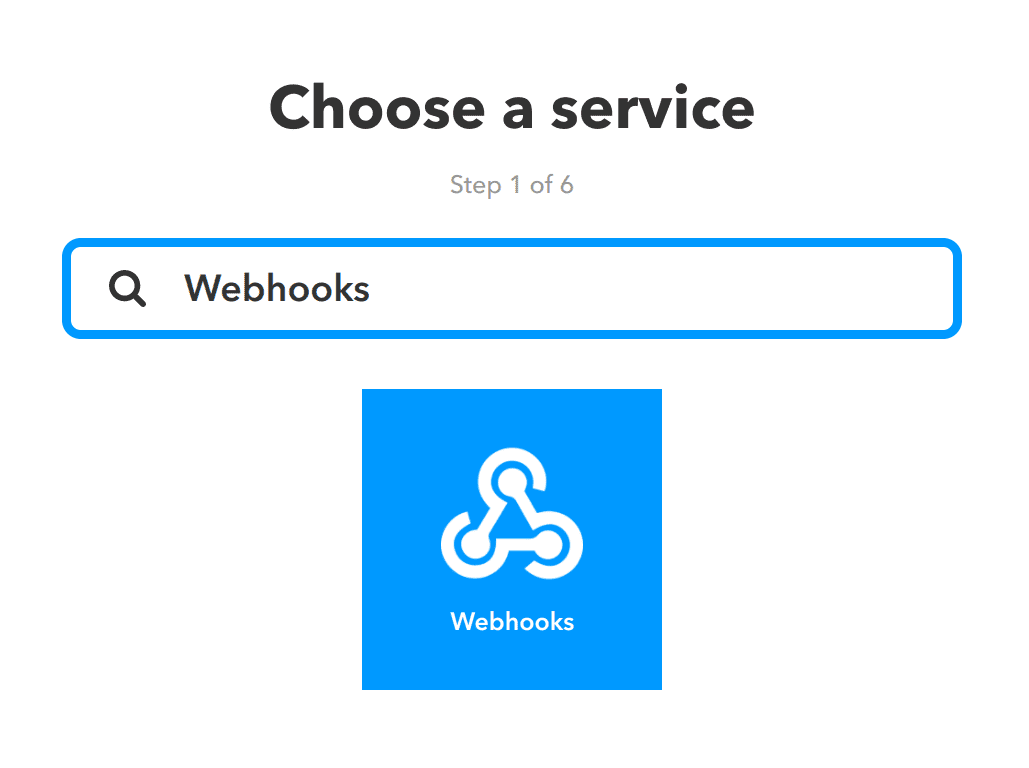
Choose Webhooks service.
Select Receive a web request.
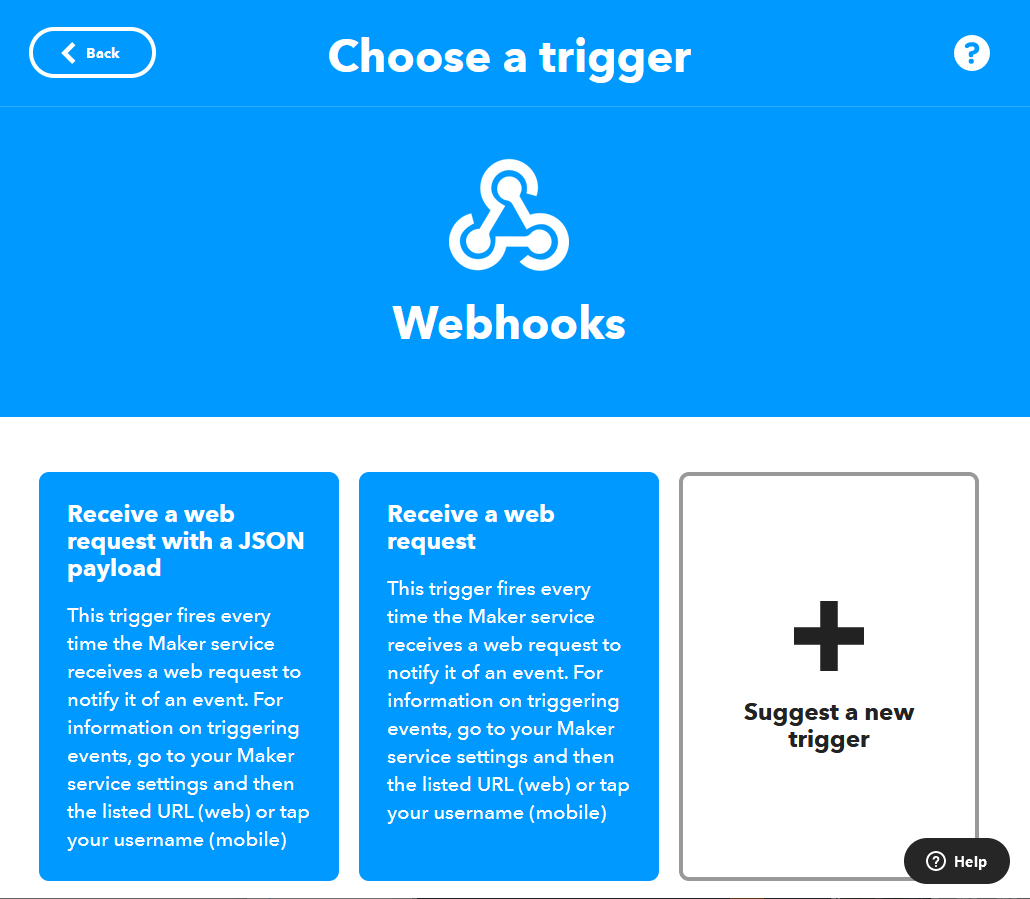
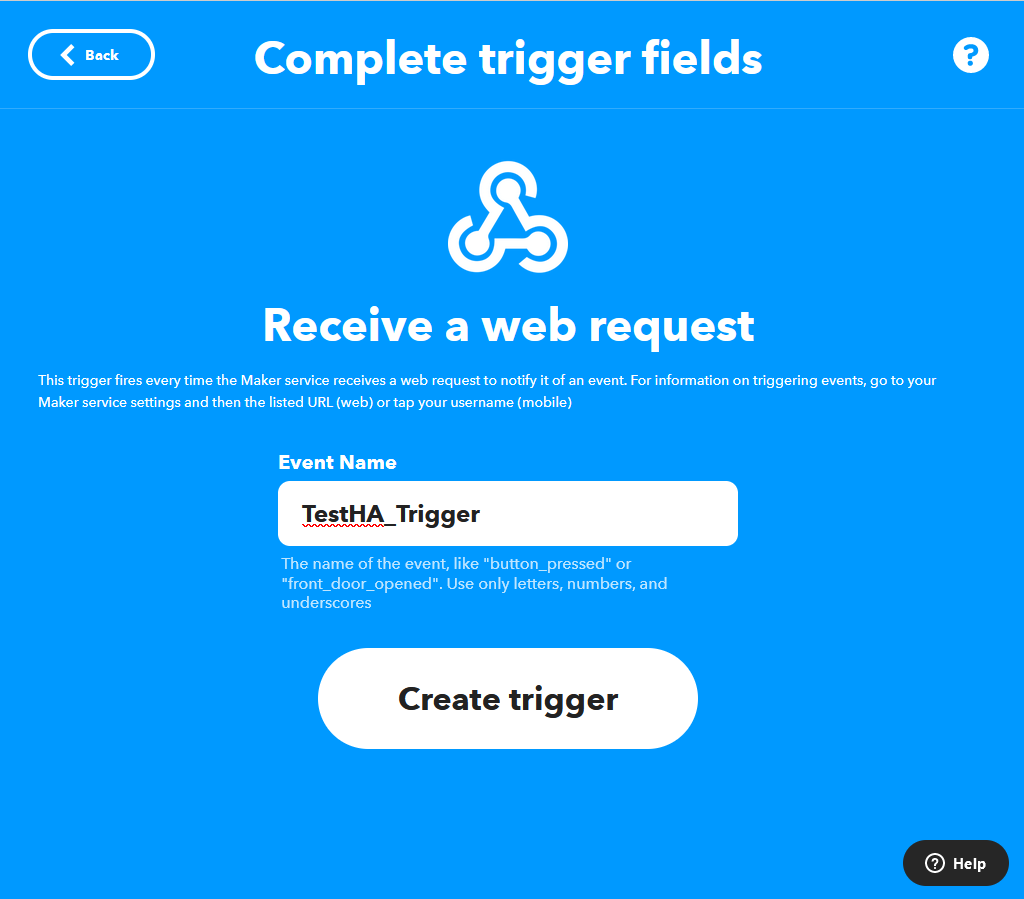
You need to setup a unique trigger for each event you sent to IFTTT.
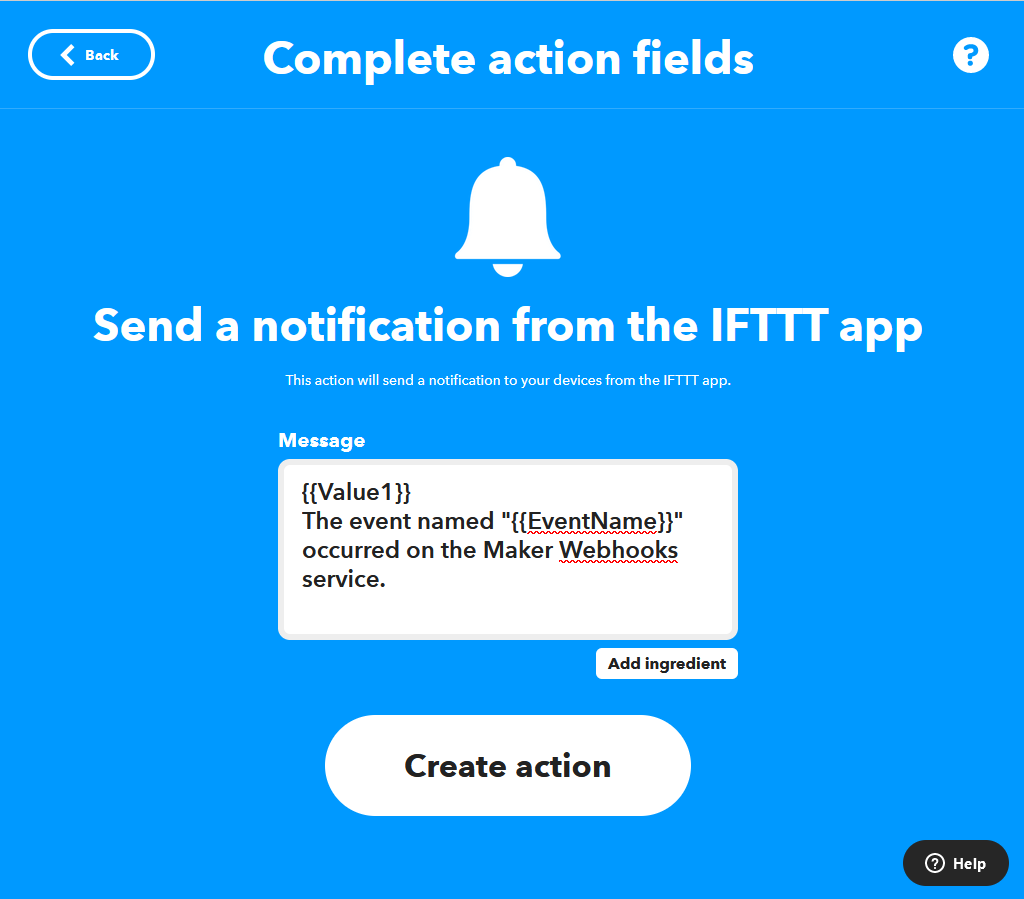
Add the Then That action. The below example sends a notification to the IFTTT mobile app and adds value1 to the message:
# Example configuration.yaml Automation entry
automation:
alias: "Startup Notification"
triggers:
- trigger: homeassistant
event: start
actions:
- action: ifttt.trigger
data: {"event":"TestHA_Trigger", "value1":"Hello World!"}
IFTTT can also be used in scripts and with templates. Here is the above automation broken into an automation and script using variables and templates.
# Example configuration.yaml Automation entry
automation:
alias: "Startup Notification"
triggers:
- trigger: homeassistant
event: start
actions:
- action: script.ifttt_notify
data:
value1: "HA Status:"
value2: "{{ trigger.event.data.entity_id.split('_')[1] }} is "
value3: "{{ trigger.event.data.to_state.state }}"
#Example Script to send TestHA_Trigger to IFTTT but with some other data (homeassistant UP).
ifttt_notify:
sequence:
- action: ifttt.trigger
data: {"event":"TestHA_Trigger", "value1":"{{ value1 }}", "value2":"{{ value2 }}", "value3":"{{ value3 }}"}